Welcome! We are super excited to see you here! We are confident that you will find TAF very helpful in providing you the valuable info about the latest updates around Quality Engineering and Test Automation tools by industry experts. Since the QA industry is transforming so rapidly around us keep visiting us to stay in sync with what’s trending…
Our Top 3 viewed Articles
We love collaborating with experienced and passionate professionals who want to share their learning from their research and implementation activities. We are very thankful to our readers/visitors for the wonderful support and encouragement around the articles that are published on TAF. Below are a few articles that most of our readers enjoy and find helpful in enhancing their automation knowledge.
Automation Tools Showcase series
Welcome to our Automation tools Showcase series! In each session, we’ll showcase an automation tool/platform from the industry and have a walkthrough (screenshare and video discussion) to introduce the tool/platform to you so that you can do a better decision making around tool/platform selection.
We don’t accept any payments/monetary favors to present a showcase review in order to promote any commercial software products. Our main intention is to expand the awareness around the testing Platforms/Products in the Software Testing/QA world so that you select the best tool for yourself independently.
- The future of test automation and How to use a Selenium Based hybrid frmwork
- How to Use a selenium based hybrid framework to achieve Continuous testing.
We are powered by MOHS10 Technologies.
At MOHS10 Technologies, we help you to achieve the desired GTM speed and cost savings for the digital transformation journey of your enterprise.
Advanced Test Automation | Performance Engineering | AI App Testing | AppSec Testing | App Dev. & Maintenance
POST YOUR ARTICLES ON TAF!
Want your Articles/Posts to be read by serious readers?
Post them on TAF and get noticed!
Test Automation forum (TAF) is turning into a popular destination for Testing and Quality Engineering professionals, Managers and senior leaders in our industry for the latest stories and innovative product showcase.
Contact us today if you have something on your mind.
We’ll be happy to help you post your article on TAF!
our latest Articles
Our Forum is continuously getting more and more popular! It’s an honor to have such talented authors who are actually contributing significantly in order to make the Forum a powerful Knowledge base for our QA Professionals worldwide.
Read through our articles to understand the latest trend in the industry and also to continuously broaden your Software Test Automation knowledge.
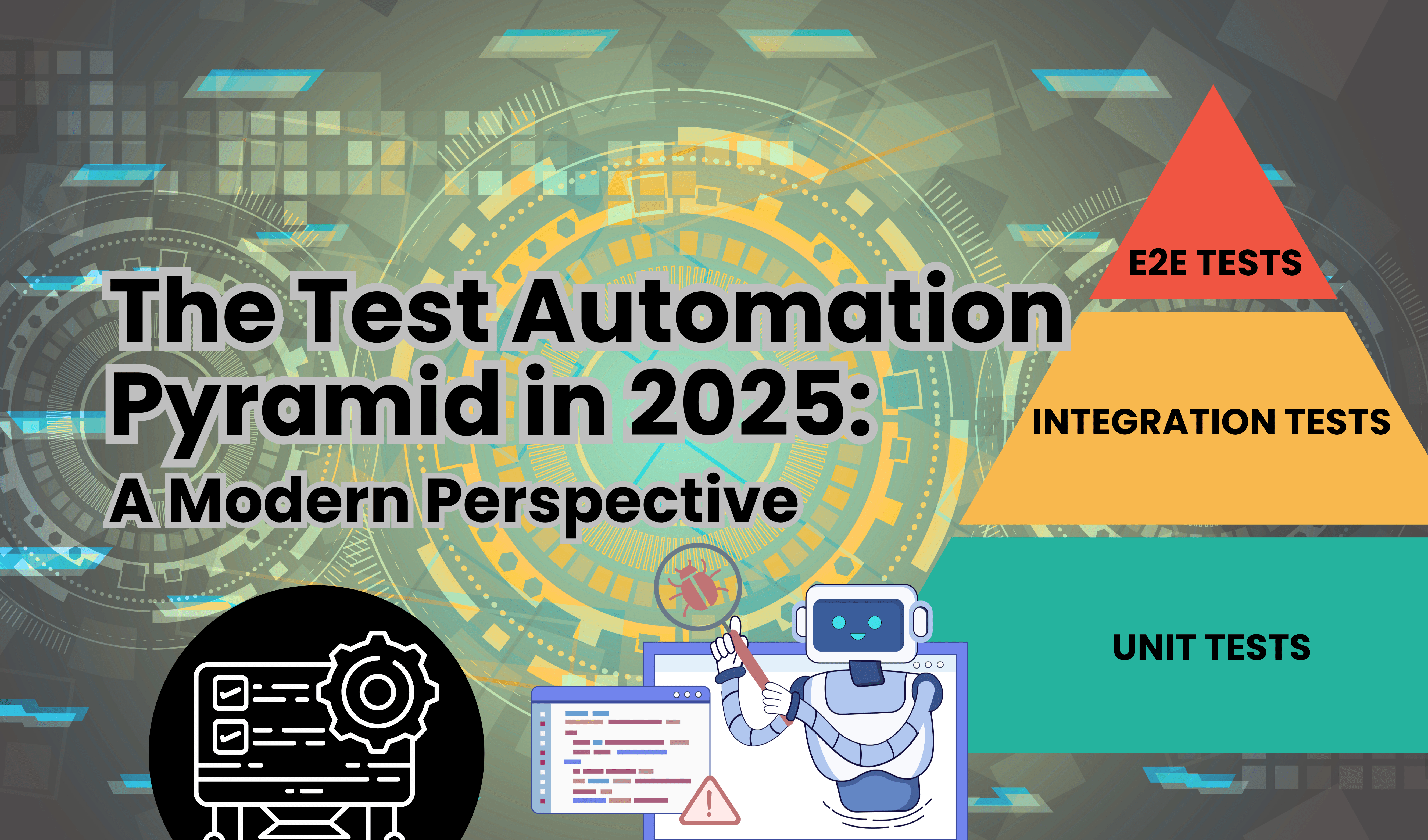
Introduction The test automation pyramid has long been a cornerstone for structuring software quality assurance. Mike Cohn’s original model advocated a broad base of unit tests, a middle layer of integration/service/API tests, and a slim top of end-to-end UI tests. Agile and DevOps teams have relied on this strategy to balance speed, coverage, and reliability. Fast forward to 2025: the pyramid continues to evolve, shaped by rising microservices adoption, cloud-native architectures, and AI-driven automation-requiring teams to rethink and modernize their approach to scalable quality. Revisiting the Foundation: Unit Tests
Introduction In an era where agility and scalability are key, microservices architecture has become the backbone of modern software systems. Its modular nature breaks down complex applications into independent services, each with its own database, business logic, and responsibilities. But with independence comes the challenge of integration. APIs act as the glue that holds microservices together, and effective API test automation is the secret to making these systems reliable and future-proof. At Mohs10 Technologies, we specialize in implementing these strategies to help organizations achieve seamless scalability. Microservices Unveiled: Why APIs
Introduction Modern software development moves at breakneck speed, with agile, DevOps, and continuous delivery making rapid releases the norm. But while code moves quickly, test coverage is often slowed by the need for specialized skills. Scriptless automation is changing everything, opening the doors for non-technical users-business analysts, manual testers, and product owners-to contribute directly to quality assurance without writing a line of code. At Mohs10 Technologies, we specialize in empowering teams with these tools to accelerate digital transformation and ensure robust software quality. What is Scriptless Automation Testing? At its
Introduction: The Dawn of Personal AI Test automation maintenance has long been the Achilles’ heel of quality assurance teams everywhere. Anyone who has managed an automation suite knows the frustration: a minor UI change breaks dozens of tests, and suddenly the team spends more time fixing scripts than actually testing functionality. This reality has led many organizations to question whether automation delivers genuine value or simply creates a different kind of technical debt. Self-healing test automation emerges as a game-changing solution to this persistent challenge. Rather than accepting broken tests
Introduction : In an era where cyber threats are increasingly sophisticated, ensuring the security of healthcare applications is paramount. This article outlines the process of conducting a vulnerability assessment and gray-box penetration testing on a healthcare application using Burp Suite Professional, OWASP ZAP, and manual testing techniques. The primary objective was to identify potential vulnerabilities …
Embracing the Future: The Evolution of Test Automation Test automation continues to be a cornerstone of quality assurance processes in the dynamic landscape of software development. As technology advances and methodologies evolve, the future of test automation promises exciting developments that will redefine how we ensure the reliability and efficiency of software systems. 1. AI …
Introduction: Test automation stands as a beacon of efficiency in the realm of software testing, promising to save both time and money. Yet, its true potential lies not just in its implementation but in the ability to yield a positive return on investment (ROI). In this article, we delve into the key strategies essential for …
Introduction: Security testing is an important aspect of software testing focused on identifying and addressing security vulnerabilities in a software application. It aims to ensure that the software is secure from malicious attacks, unauthorized access, and data breaches. Security testing involves verifying the software’s compliance with security standards, evaluating the security features and mechanisms, and …